Transmittance Equation - Can Absorbance Value Be Greater Than 1?

Transmittance equation
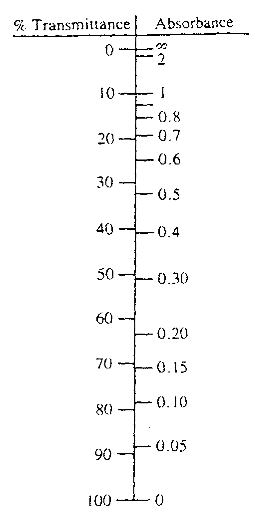
For most spectrometers and colorimeters, the useful absorbance range is from 0.1 to 1. Absorbance values greater than or equal to 1.0 are too high. If you are getting absorbance values of 1.0 or above, your solution is too concentrated.
How is concentration related to absorbance and transmittance?
One factor that influences the absorbance of a sample is the concentration (c). The expectation would be that, as the concentration goes up, more radiation is absorbed and the absorbance goes up. Therefore, the absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration.
What is the absorbance when the transmittance is 30?
| Transmittance | Absorbance (AU) |
|---|---|
| 40% | 0.398 |
| 35% | 0.456 |
| 30% | 0.523 |
| 25% | 0.602 |
How do you solve for absorbance?
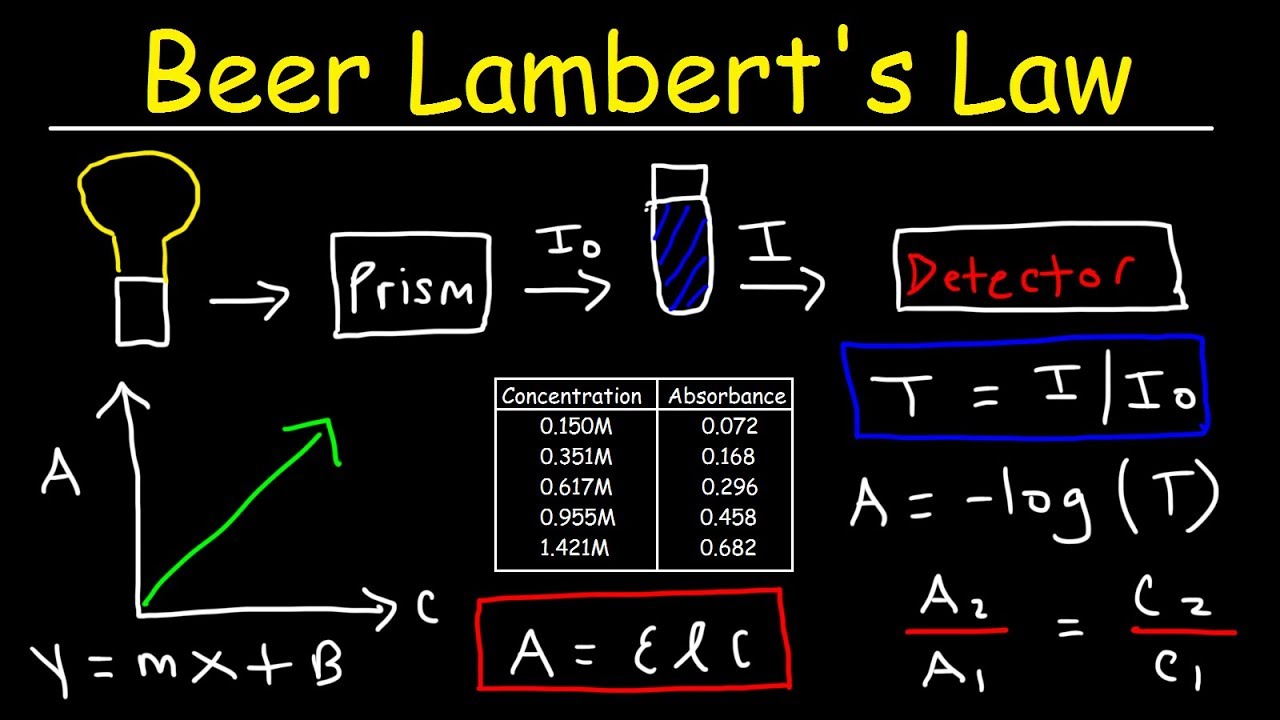
Equations & Definitions for Finding the Absorbance of a Solution Using the Beer-Lambert Law
- Beer's Law equation : A = ε bC.
- Absorbance: The amount of light absorbed by a solution as light passes through this solution.
- Molar Absorptivity: A measure of how strong a particular substance absorbs light.
How do you use the c1v1 c2v2 equation?
The formula for calculating a dilution is (C1) (V1) = (C2) (V2) where...
- C1 is the concentration of the starting solution.
- V1 is the volume of the starting solution.
- C2 is the concentration of the final solution.
- V2 is the volume of the final solution.
What is path length in Beer's law?
The path length in the Beer-Lambert law is the length through which light travels in a solution.
Why is transmittance measured instead of absorbance?
Absorbance is used more often than percent transmittance because this variable is linear with the concentration of the absorbing substance, whereas percent transmittance is exponential.
How do I calculate the concentration of a solution?
Divide the mass of the solute by the total volume of the solution. Write out the equation C = m/V, where m is the mass of the solute and V is the total volume of the solution. Plug in the values you found for the mass and volume, and divide them to find the concentration of your solution.
How do I get transmittance?
Transmittance (T) is the fraction of incident light which is transmitted. In other words, it's the amount of light that “successfully” passes through the substance and comes out the other side. It is defined as T = I/Io, where I = transmitted light (“output”) and Io = incident light (“input”).
How is Beer's Law calculated?
The equation for Beer's law is a straight line with the general form of y = mx +b. where the slope, m, is equal to εl. In this case, use the absorbance found for your unknown, along with the slope of your best fit line, to determine c, the concentration of the unknown solution.
What is the unit for absorbance in Beer's law?
What is the unit of absorbance in Beer's law? The absorbance is a unitless quantity. It is the ratio of the intensity of the incident light and the transmitted light; hence, it is dimensionless and has no units.
Is transmittance the same as absorbance?
Absorbance and transmittance are two related, but different quantities used in spectrometry. The main difference between absorbance and transmittance is that absorbance measures how much of an incident light is absorbed when it travels in a material while transmittance measures how much of the light is transmitted.
How do you calculate transmittance from absorbance?
To convert a value from percent transmittance (%T) to absorbance, use the following equation: Absorbance = 2 – log(%T) Example: convert 56%T to absorbance: 2 – log(56) = 0.252 absorbance units.
How do you calculate Beer-Lambert Law?
The Beer–Lambert law relates the absorption of light by a solution to the properties of the solution according to the following equation: A = εbc, where ε is the molar absorptivity of the absorbing species, b is the path length, and c is the concentration of the absorbing species.
What is transmittance and absorbance?
Absorbance (A), also known as optical density (OD), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. Transmittance is the quantity of light that passes through a solution.
How do you calculate concentration from transmittance?
Absorbance Measurements – the Quick Way to Determine Sample Concentration
- Transmission or transmittance (T) = I/I0
- Absorbance (A) = log (I0/I)
- Absorbance (A) = C x L x Ɛ => Concentration (C) = A/(L x Ɛ)
Can absorbance be negative?
Negative Absorbance Readings Sample measurements read negative absorbance for the following reasons: The absorbance value of the reference is higher than the sample. The reference and the sample are interchanged. The sample is very dilute and close to the absorbance of the reference.
What is Beer's law spectrophotometry?
The amount of light absorbed by a solution is related to the analyte concentration by the Beer–Lambert law, which is expressed as follows: A = εbc, where ε is the molar absorptivity of the analyte, b is the path length (the distance the light travels through the solution), and c is the concentration of the analyte.
What is internal transmittance?
Internal transmittance refers to transmittance measured by excluding reflection losses at the entrance and exit surfaces of a glass for a given thickness such as 5mm or 10mm with a wavelength range from 280nm to 2550nm. Optical glasses have an excellent transmittance from the visible region to the near IR region.
What is transmittance what is its unit?
6.2. Transmittance is the transmission-mode analog to the reflectance. That is, transmittance is a dimensionless number defined by the ratio of the radiant flux Φt transmitted to the incident radiant flux Φi, (6.6)

Post a Comment for "Transmittance Equation - Can Absorbance Value Be Greater Than 1?"