What Is Pwm In Electronics - What Is PWM And Its Advantages?

What is pwm in electronics
The main advantage of PWM is that power loss in the switching devices is very low. When a switch is off there is practically no current, and when it is on and power is being transferred to the load, there is almost no voltage drop across the switch.
What is PWM in simple words?
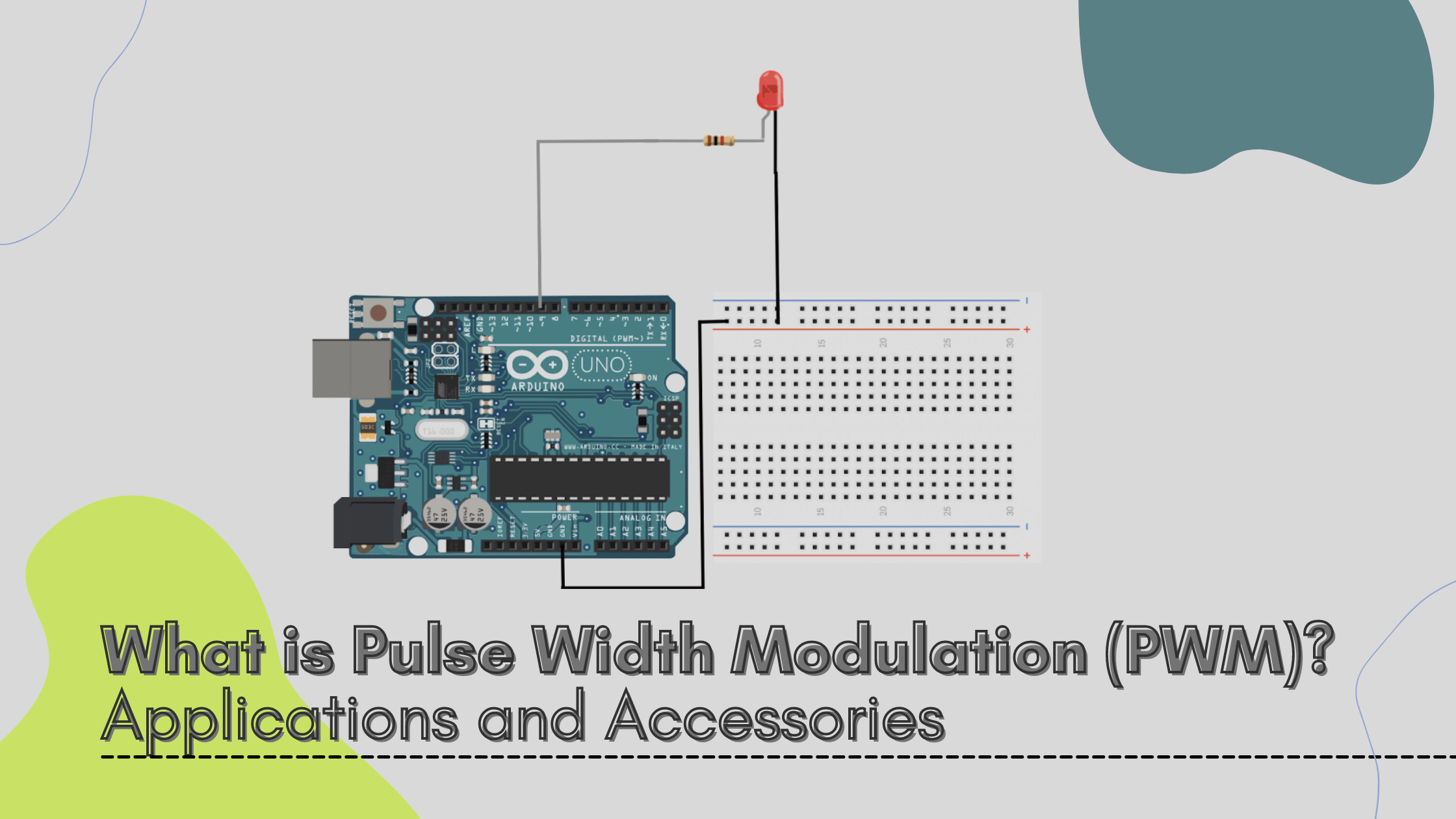
Pulse width modulation or PWM is a commonly used control technique that generates analog signals from digital devices such as microcontrollers. In PWM technique, the signal's energy is distributed through a series of pulses rather than a continuously varying (analog) signal.
Is PWM better than voltage?
First, the PWM voltage that your motor will see will have high frequency harmonics. These harmonics will introduce losses in your motor that wouldn't be there if you were using DC voltage. What this means is that your motor will get hotter when with PWM vs. DC (all other things being equal).
How does PWM control voltage?
Driving a cooling fan motor with PWM causes the motor to respond to the average of the pulses. In this way, PWM mimics the linear control obtained through varying a voltage that changes over time. The average voltage equals duty cycle multiplied by the maximum voltage applied to the motor.
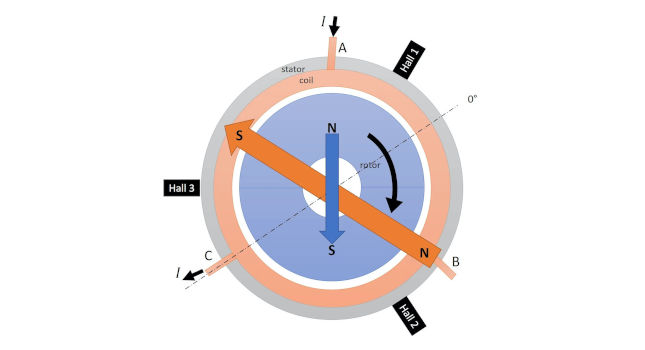
Why is PWM used in motors?
Motors as a class require very high currents to operate. Being able to vary their speed with PWM increases the efficiency of the total system by quite a bit. PWM is more effective at controlling motor speeds at low RPM than linear methods.
What are 3 types of motor controls?
There are four basic motor controller and drive types: AC, DC, servo, and stepper, each having an input power type modified to the desired output function to match with an application.
What is the main disadvantage of PWM?
Stroboscopic effect evident in fast moving environments when the driver frequency is low. Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) issues due to rise and fall of the current in PWM dimming.
Is a PWM signal DC or AC?
PWM is dc, on and off, not sine wave, no ac content no rms values etc. etc. If you apply 50% duty from a 5v source then the average output is 2.5v. The scope will show 5v pulses.
What are the types of PWM?
There are three conventional types of PWM techniques namely: Lead Edge Modulation. Trail Edge Modulation. Pulse Center Two Edge Modulation/Phase Correct PWM.
Which wire is PWM?
Blue (or green) is the PWM input.
What happens if PWM frequency is too high?
At higher PWM frequencies, the pulses from the motor controller board change too quickly to provide enough energy to spin the motor until the equivalent voltage reaches 2.0 volts, although switching to using slow decay mode can help.
What is PWM and how it works?
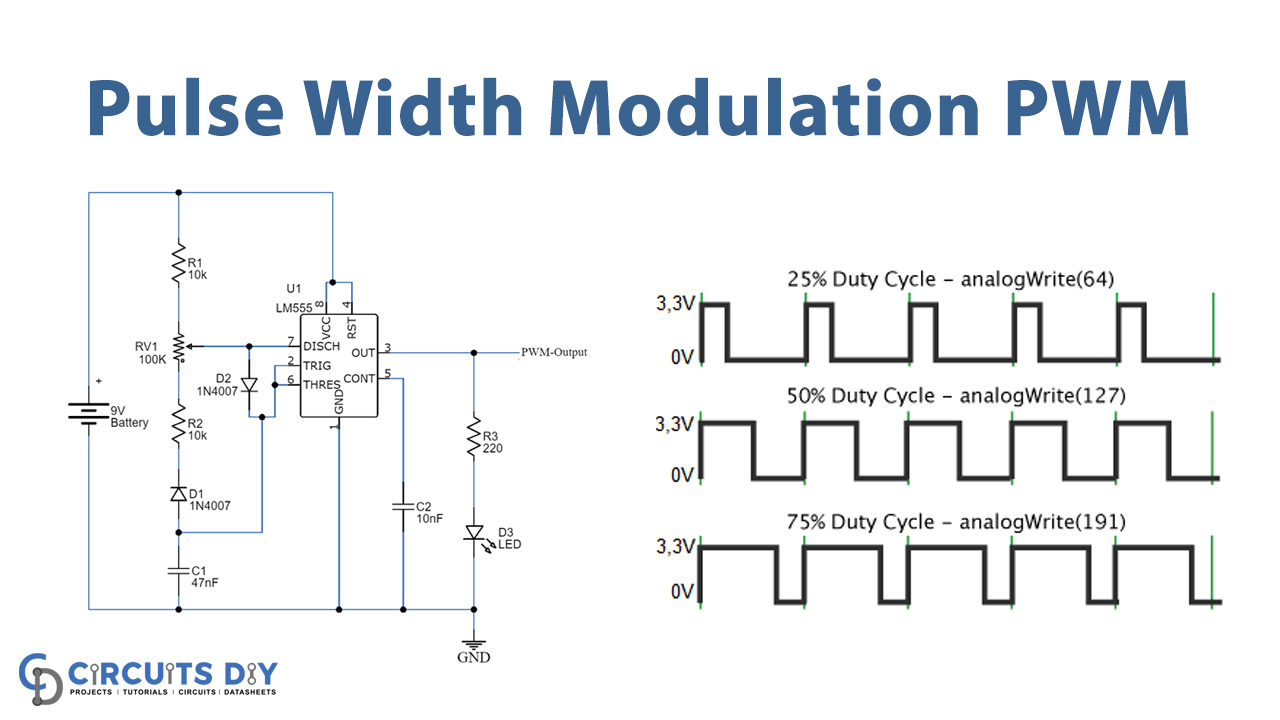
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a technique to generate low frequency output signals from high frequency pulses. Rapidly switching the output voltage of an inverter leg between the upper and lower DC rail voltages, the low frequency output can be thought of as the average of voltage over a switching period.
Is PWM digital or analog?
The PWM signal is still digital because, at any given instant of time, the full DC supply is either fully on or fully off. The voltage or current source is supplied to the analog load by means of a repeating series of on and off pulses.
How does PWM save power?
PWM or Pulse Width Modulation, is one method that can be used to control the speed of a fan. This technique works by rapidly cycling a fixed-voltage power supply between the on and off condition, thereby reducing the overall amount of energy provided to the fan.
How is PWM signal generated?
PWM signal can be generated using a comparator. One input of the comparator is connected to a modulating signal and the other input is fed with a non-sinusoidal wave or saw-tooth wave. The comparator compares the two input signals and generates a PWM signal.
Why is PWM used with LEDS?
PWM is a very common method of dimming LED lights that works by very rapidly turning them on and off (pulsing) for periods that visually appear as a steady dimmed light. We adjust the brightness level by adjusting the percentage of the time the lights are on (100%) to the time they are off (0%).
What is the frequency of PWM?
PWM Frequency Typically, a servo motor anticipates an update every 20 ms with a pulse between 1 ms and 2 ms. This equates to a duty cycle of 5% to 10% at 50 Hz.
Is PWM positive or negative?
Set the polarity of the PWM signal. By default, this value is Positive , which sets the digital pulse high (on) for the duty-cycle, and off for the remainder of the period. Setting polarity to Negative sets the digital pulse low (off) for the duty-cycle, and on for the remainder of the period.
Which PWM technique is best?
The simulation result shows that THIPWM exhibits the best induction motor drive performance compared to other PWM techniques. Using THIPWM, effect of high carrier frequency on rotor current, stator current, electromagnetic torque etc. is also presented here.
Is PWM a sensor?
PWM stands for (Pulse Width Modulation) and it is the communication system that modulates the changed duty ratio of the pulse wave. It does not change the voltage magnitude and the cycle but only the width of the high level (ON) of the pulse is changed.





![Pulse Width Modulation[PWM] Working, Applications, Advantages ...](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgOJhUYLLJCmdwmE6aqUUMNqaWovF1fjIMoy35jfqH85iyop43T_WTK_66A7Em4ovTthEknyp3CeBpX0HQMpCWfg9A4QXVpTw4-1LI7qF3PyB1GmTeGntOWvvqAZOuMwxOJoFCuDh8_3yik/s1600/electronic+pulse.png)

Post a Comment for "What Is Pwm In Electronics - What Is PWM And Its Advantages?"