Manchester Encoding - What Would Be The Minimum Bandwidth Of Manchester Coding?

Manchester encoding
The Manchester scheme needs a minimum bandwidth of 1 MHz. The first choice needs a lower bandwidth, but has a DC component problem; the second choice needs a higher bandwidth, but does not have a DC component problem.
What is bipolar line coding?
In telecommunication, bipolar encoding is a type of return-to-zero (RZ) line code, where two nonzero values are used, so that the three values are +, −, and zero. Such a signal is called a duobinary signal. Standard bipolar encodings are designed to be DC-balanced, spending equal amounts of time in the + and − states.
Why is Manchester encoding better than NRZ?
Manchester is an NRZ encoding that is exclusively-ORed with the clock. This provides at least one transition per bit. NRZI also uses a transition in the middle of the clock cycle, but this only occurs when there is a 1 value. Manchester makes clock recovery easier.
What is difference between bit rate and baud rate?
The Baud rate refers to the total number of signal units transmitted in one second. The Bit rate refers to the total Bits transmitted in one unit time. Baud rate indicates the total number of times the overall state of a given signal changes/ alters. Bit rate indicates the total bits that travel per second.
What is the difference between Polar Return to Zero and Manchester line coding?
The main difference is that polar NRZ-L uses a negative voltage to represent binary one and a positive voltage to represent binary zero, whereas Manchester uses a positive-to-negative transition to represent binary one and a negative-to-positive transition to represent binary zero.
What is biphase encoding?
Bi-phase encoding involves double-checking of the signal. Signals are checked at the beginning and in the middle. Due to double-checking of the signal, the clock rate is twice the rate of data transfer. The clock synchronization is taken from the signal; hence it requires a greater bandwidth.
Why is Manchester encoding more popular than the other types of encoding?
Manchester Code Has Advantages One of the major benefits of the Manchester code is that it avoids some of the problems of the non-return-to-zero (NRZ) encoding. There, during each bit period, a logic '1' is represented by a “high”-level, and a logic '0' by a “low”-level.
In which encoding do we use three levels?
MLT-3 encoding (Multi-Level Transmit) is a line code (a signaling method used in a telecommunication system for transmission purposes) that uses three voltage levels.
What is line coding techniques?
A line code is the code used for data transmission of a digital signal over a transmission line. This process of coding is chosen so as to avoid overlap and distortion of signal such as inter-symbol interference.
What are different types of polar encoding?
Several types: NRZ, RZ, and biphase. Polar encoding uses two voltage levels (positive and negative).
What is 4b 5b encoding?
4b/5b encoding is a type of 'Block coding'. This processes groups of bits rather than outputting a signal for each individual bit (as in Manchester encoding). A group of 4 bits is encoded so that an extra 5th bit is added. Since the input data is taken 4-bits at a time, there are 2^4, or 16 different bit patterns.
What is meant by Manchester encoding?
In data transmission, Manchester encoding is a form of digital encoding in which data bits are represented by transitions from one logical state to the other. This is different from the more common method of encoding, in which a bit is represented by either a high state such as +5 volts or a low state such as 0 volts.
How does bipolar signaling differ from unipolar signaling Why is Manchester encoding more popular than either?
In Manchester signaling, voltage is positive or negative and bits are indicated by a mid-bit transition. Manchester is more popular than bipolar and unipolar because errors are easily detectable by missing mid-signal transition.
Which of the following is true about Manchester encoding?
It requires more bandwidth than 8B/10B encoding.
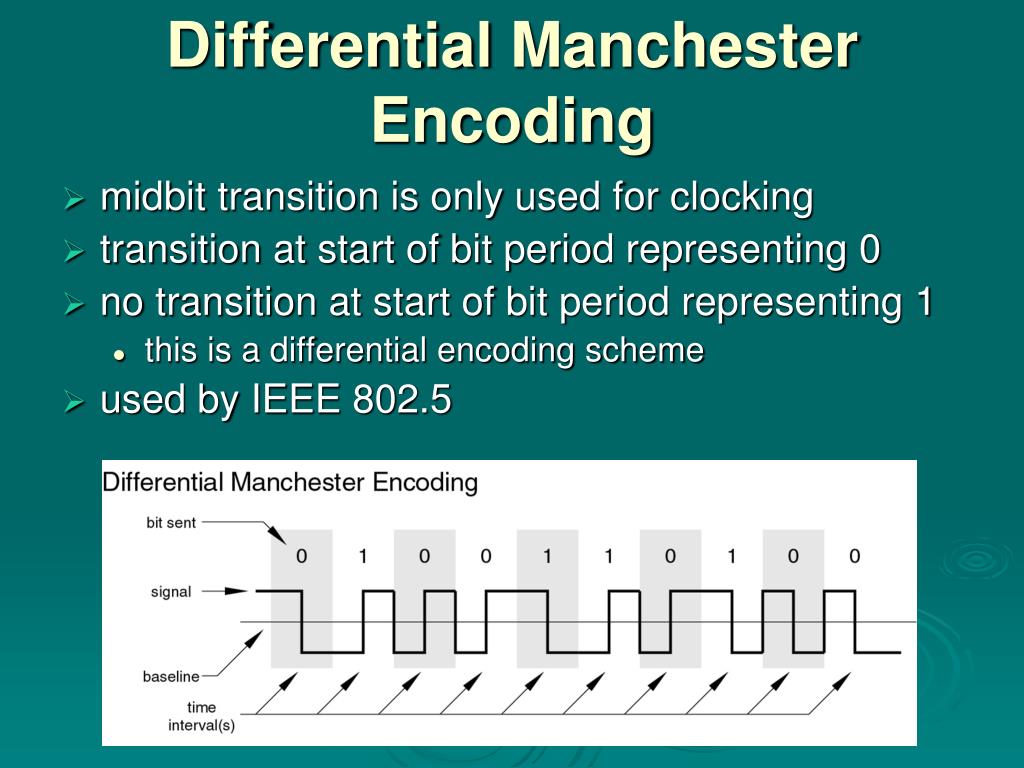
What is differential Manchester encoding in computer networks?
Differential Manchester encoding (DM) is a line code in digital frequency modulation in which data and clock signals are combined to form a single two-level self-synchronizing data stream.
What do you mean by modulation?
Modulation is the process of converting data into radio waves by adding information to an electronic or optical carrier signal. A carrier signal is one with a steady waveform -- constant height, or amplitude, and frequency.
What is baud rate?
The baud rate is the rate at which information is transferred in a communication channel. Baud rate is commonly used when discussing electronics that use serial communication. In the serial port context, "9600 baud" means that the serial port is capable of transferring a maximum of 9600 bits per second.
Where is Manchester encoding used in data communications?
Manchester encoding is used as the physical layer of an Ethernet LAN, where the additional bandwidth is not a significant issue for coaxial cable transmission, the limited bandwidth of CAT5e cable necessitated a more efficient encoding method for 100 Mbps transmission using a 4b/5b MLT-3 code.
What are the 3 techniques of digital to digital techniques?
The conversion involves three techniques: line coding, block coding, and scrambling.
What are the three types of bipolar encoding?
The bipolar encoding scheme defines three voltage methods: positive, negative, and zero. In the Bipolar encoding scheme, zero levels define binary 0, and binary 1 is described by rotating positive and negative voltages.





Post a Comment for "Manchester Encoding - What Would Be The Minimum Bandwidth Of Manchester Coding?"